Dense 3D Semantic Mapping of Indoor Scenes from RGB-D Images
Alexander Hermans, Georgios Floros, Bastian Leibe
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2014) - Best Vision Paper Award
|
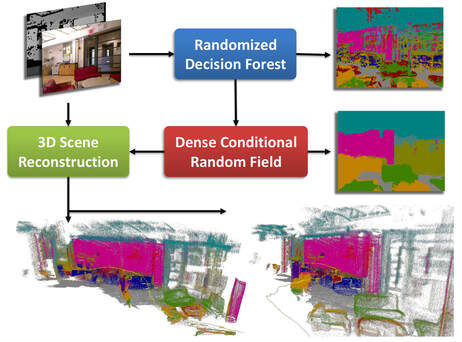
Dense semantic segmentation of 3D point clouds is a challenging task. Many approaches deal with 2D semantic segmentation and can obtain impressive results. With the availability of cheap RGB-D sensors the field of indoor semantic segmentation has seen a lot of progress. Still it remains unclear how to deal with 3D semantic segmentation in the best way. We propose a novel 2D-3D label transfer based on Bayesian updates and dense pairwise 3D Conditional Random Fields. This approach allows us to use 2D semantic segmentations to create a consistent 3D semantic reconstruction of indoor scenes. To this end, we also propose a fast 2D semantic segmentation approach based on Randomized Decision Forests. Furthermore, we show that it is not needed to obtain a semantic segmentation for every frame in a sequence in order to create accurate semantic 3D reconstructions. We evaluate our approach on both NYU Depth datasets and show that we can obtain a significant speed-up compared to other methods.
|
OpenStreetSLAM: Global Vehicle Localization Using OpenStreetMaps
Georgios Floros, Benito van der Zander, Bastian Leibe
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2013)
|
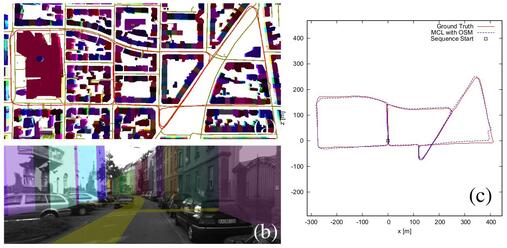
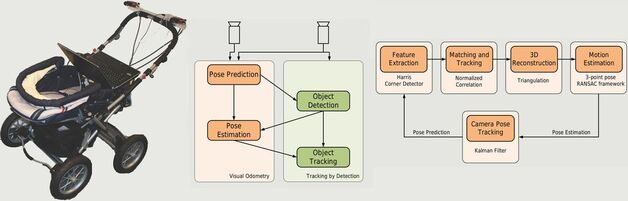
In this paper we propose an approach for global vehicle localization that combines visual odometry with map information from OpenStreetMaps to provide robust and accurate estimates for the vehicle’s position. The main contribution of this work comes from the incorporation of the map data as an additional cue into the observation model of a Monte Carlo Localization framework. The resulting approach is able to compensate for the drift that visual odometry accumulates over time, significantly improving localization quality. As our results indicate, the proposed approach outperforms current state-of-the-art visual odometry approaches, indicating in parallel the potential that map data can bring to the global localization task.
|
Joint 2D-3D Temporally Consistent Semantic Segmentation of Street Scenes
Georgios Floros, Bastian Leibe
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2012)
|
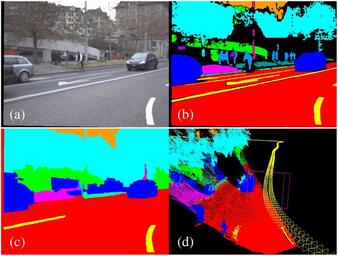
In this paper we propose a novel Conditional Random Field (CRF) formulation for the semantic scene labeling problem which is able to enforce temporal consistency between consecutive video frames and take advantage of the 3D scene geometry to improve segmentation quality. The main contribution of this work lies in the novel use of a 3D scene reconstruction as a means to temporally couple the individual image segmentations, allowing information flow from 3D geometry to the 2D image space. As our results show, the proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods and opens a new perspective towards a tighter interplay of 2D and 3D information in the scene understanding problem.
|
Multi-Class Image Labeling with Top-Down Segmentation and Generalized P^N Potentials
Georgios Floros, Konstantinos Rematas, Bastian Leibe
British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2011)
|
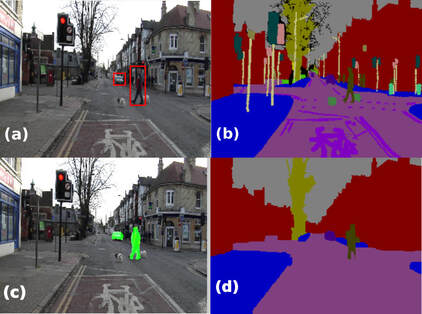
We propose a novel formulation for the scene labeling problem which is able to combine object detections with pixel-level information in a Conditional Random Field (CRF) framework. Since object detection and multi-class image labeling are mutually informative problems, pixel-wise segmentation can benefit from powerful object detectors and vice versa. The main contribution of the current work lies in the incorporation of top-down object segmentations as generalized robust P N potentials into the CRF formulation. These potentials present a principled manner to convey soft object segmentations into a unified energy minimization framework, enabling joint optimization and thus mutual benefit for both problems. As our results show, the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the categories for which object detections are available. Quantitative and qualitative experiments show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
|
Real Time Vision Based Multi-Person Tracking for Mobile Robotics and Intelligent Vehicles
Dennis Mitzel, Georgios Floros, Patrick Sudowe, Benito van der Zander, Bastian Leibe
International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications (ICIRA 2011)
|
In this paper, we present a real-time vision-based multi-person tracking system working in crowded urban environments. Our approach combines stereo visual odometry estimation, HOG pedestrian detection, and multi-hypothesis tracking-by-detection to a robust tracking framework that runs on a single laptop with a CUDA-enabled graphics card. Through shifting the expensive computations to the GPU and making extensive use of scene geometry constraints we could build up a mobile system that runs with 10Hz. We experimentally demonstrate on several challenging sequences that our approach achieves competitive tracking performance.
|
Modulating the Shape and Size of Backprojection Surfaces to Improve Accuracy in Volumetric Stereo
Xenophon Zabulis, Georgios Floros
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, Volume 2009
|
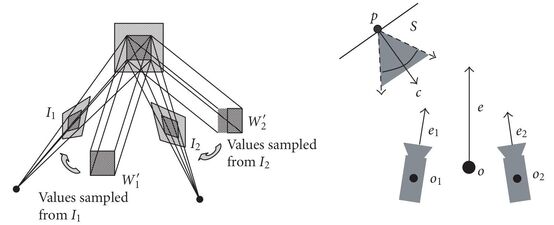
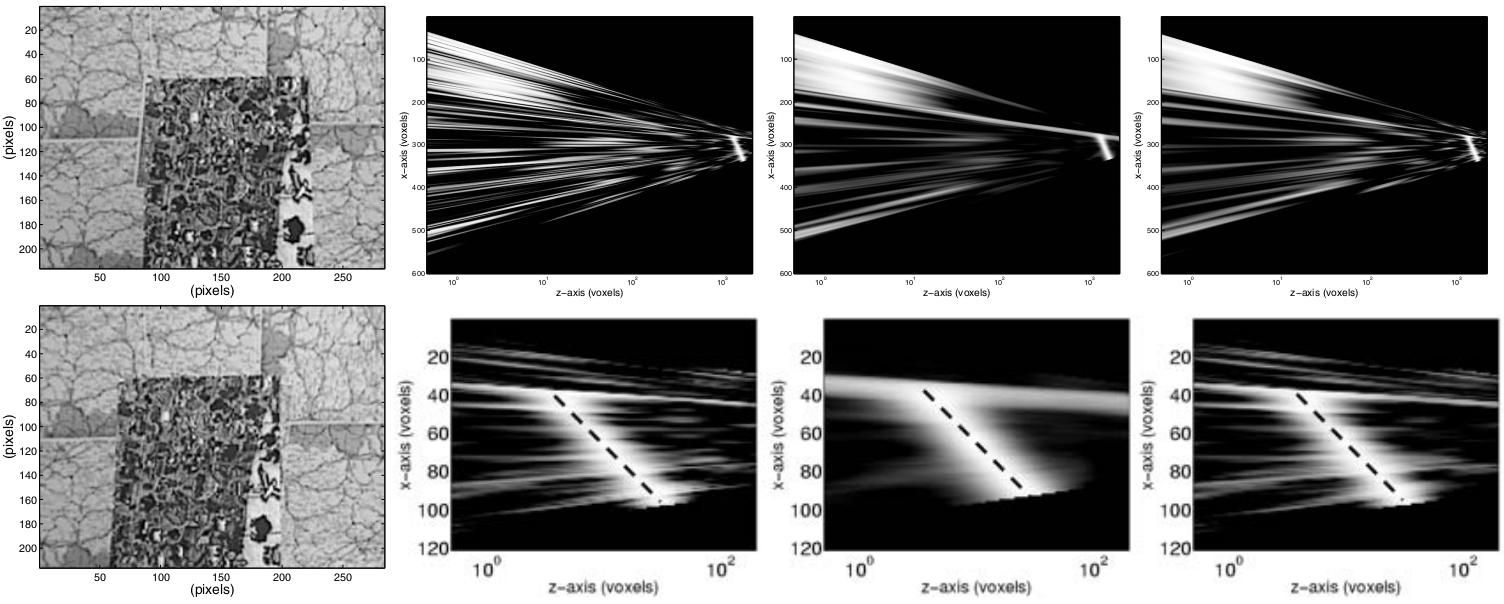
In 3D TV applications, the extraction of 3D representations of dynamic scenes from images plays a central role in the preparation of the presented visual content. This paper focuses on the stereo cue to the extraction of these representations and, in particular, on the recently developed family of volumetric approaches to stereo. Two methods are proposed that improve the accuracy of volumetric stereo approaches, which compare backprojections of image regions to establish stereo correspondences. The proposed methods are based on maximizing the utilization of the available image resolution, as well as, equalizing the sampled image area across pairs of image regions that are compared.
|
An efficient and memory-conserving implementation of multi-view stereo for wide-area reconstruction
Xenophon Zabulis, Nikos Grammalidis, Georgios Floros
International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization and Transmission (3DPVT 2008)
|
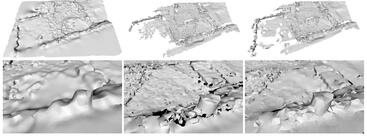
This paper deals with the automatic stereo reconstruction of wide-area scenes. Its particular goal is a computationally efficient method that can be performed on a personal computer, despite the large amount of data involved in the reconstruction of wide-area scenes. Robustness is considered in terms of the accuracy of the final reconstruction, as well as, in the context of simplifying the image acquisition process for the end-user.
|
Modulating the Size of Backprojection surface patches, in volumetric stereo, for increasing reconstruction accuracy and robustness
Xenophon Zabulis, Georgios Floros
3DTV Conference 2007
|
This paper concerns volumetric stereo methods, which compare the backprojections of the acquired images onto a hypothetical surface patch in order to reconstruct the imaged surfaces. In particular, it introduces a size-modulation of this patch so that its projection area in the acquired images is invariant to distance and rotation. It is shown, and explained why, that performing this modulation results in superior accuracy of the volumetric reconstruction than retaining the patch size constant, as it has been to date practiced. The proposed extension to the hypothetical patch operator is compatible with the existing volumetric approaches to stereo.
|